The Modern AI Development Stack
Lesson Video:
In 2024, if you wanted AI assistance while coding, you had to choose: Do I use GitHub Copilot in VS Code? Or ChatGPT in a browser? Or Claude in a separate window?
Each tool lived in its own silo. You couldn't easily combine them. You couldn't swap one model for another without rewriting your entire workflow. And if your preferred vendor changed their pricing or shut down a feature? You were stuck.
2025 changed that.
The modern AI development stack is no longer a single tool. It's a three-layer architecture that separates concerns, enables interoperability, and gives you control. Understanding this stack is essential because it shapes how you'll work for the next five years.
This section explains the three layers, what makes 2025's stack fundamentally different from 2024's, and how to choose the right tools for your context.
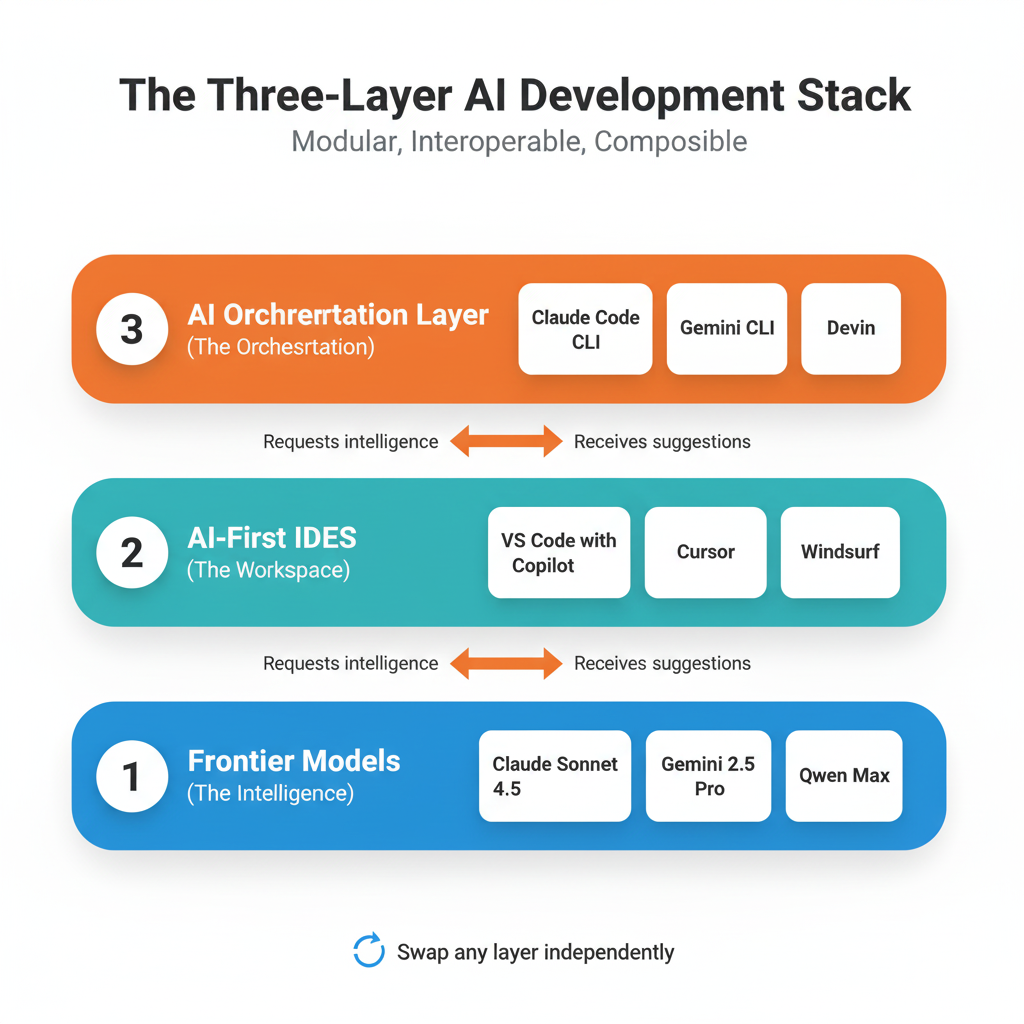
The Three-Layer AI Development Stack
Think of the modern AI development stack like a building with three floors, each serving a distinct purpose:
Layer 1: Frontier Models (The Intelligence)
What it is: The large language models that provide reasoning, code generation, and understanding. Examples: GPT-5, Claude Opus 4, Gemini 2.5 Pro, Qwen Code.
What it does: This layer handles the "thinking." When you ask for code suggestions, explanations, or debugging help, the frontier model processes your request and generates responses.
Why it's separate: Models improve constantly. New ones appear every few months. By keeping this layer separate, you can swap models without changing your workflow. Today you use Claude Opus 4; tomorrow, GPT-6 launches with better performance—you switch models, not tools.
In practice: You don't interact with this layer directly. You access it through Layer 2.
Layer 2: AI-First IDEs (The Workspace)
What it is: Integrated Development Environments designed for AI-assisted work. Examples: VS Code with Copilot, Cursor, Windsurf, JetBrains with AI Assistant.
What it does: This layer provides the interface where you write code and interact with AI. It handles context gathering (what files are open, what you're working on), presents AI suggestions inline, and manages the conversation history.
Why it's separate: Different developers prefer different environments. Some love VS Code's ecosystem. Others prefer JetBrains' IntelliJ for Java. By separating the IDE from the intelligence, you choose your preferred interface without being locked into a specific model.
In practice: This is where you spend your day. You write code, ask questions, and review suggestions—all within your familiar editor.
Layer 3: Development Agents (The Orchestration)
What it is: Autonomous agents that execute multi-step tasks on your behalf. Examples: Claude Code CLI, Aider, GitHub Copilot Workspace, Devin.
What it does: This layer handles complex, multi-step workflows: refactoring entire modules, running tests, creating pull requests, debugging across multiple files. Unlike Layer 2 (which suggests code line-by-line), Layer 3 agents can autonomously execute entire tasks.
Why it's separate: Not every task needs autonomous execution. Sometimes you want suggestions (Layer 2). Sometimes you want the AI to handle the entire workflow (Layer 3). Separating these layers gives you control over when to use which approach.
In practice: You invoke an agent with a high-level task ("refactor the authentication module to use JWT tokens") and let it execute autonomously while you review the changes.
How the Layers Work Together
Here's a typical workflow combining all three layers:
- You're coding in VS Code (Layer 2: AI-First IDE / Workspace) working on a feature.
- VS Code sends your code to Claude Opus 4 (Layer 1: Frontier Model) for inline suggestions.
- You accept suggestions, write code, and reach a complex refactoring task.
- You invoke Claude Code CLI (Layer 3: Development Agent) to autonomously refactor three files, run tests, and verify the changes.
- Claude Code CLI uses Claude Opus 4 (Layer 1) for reasoning but executes autonomously without you watching every step.
Each layer has a clear job. You can swap any layer without breaking the others.
Explore the stack through YOUR workflow: Think about how you currently use AI tools (or plan to). Ask your AI partner: "Based on how I described my workflow, which layer am I using most? Which layer am I NOT using but could benefit from?" Let your AI help you discover gaps in how you're leveraging the three-layer architecture through dialogue about your actual practices.
What Makes 2025 Different from 2024
The three-layer stack didn't exist in 2024. Here's what changed:
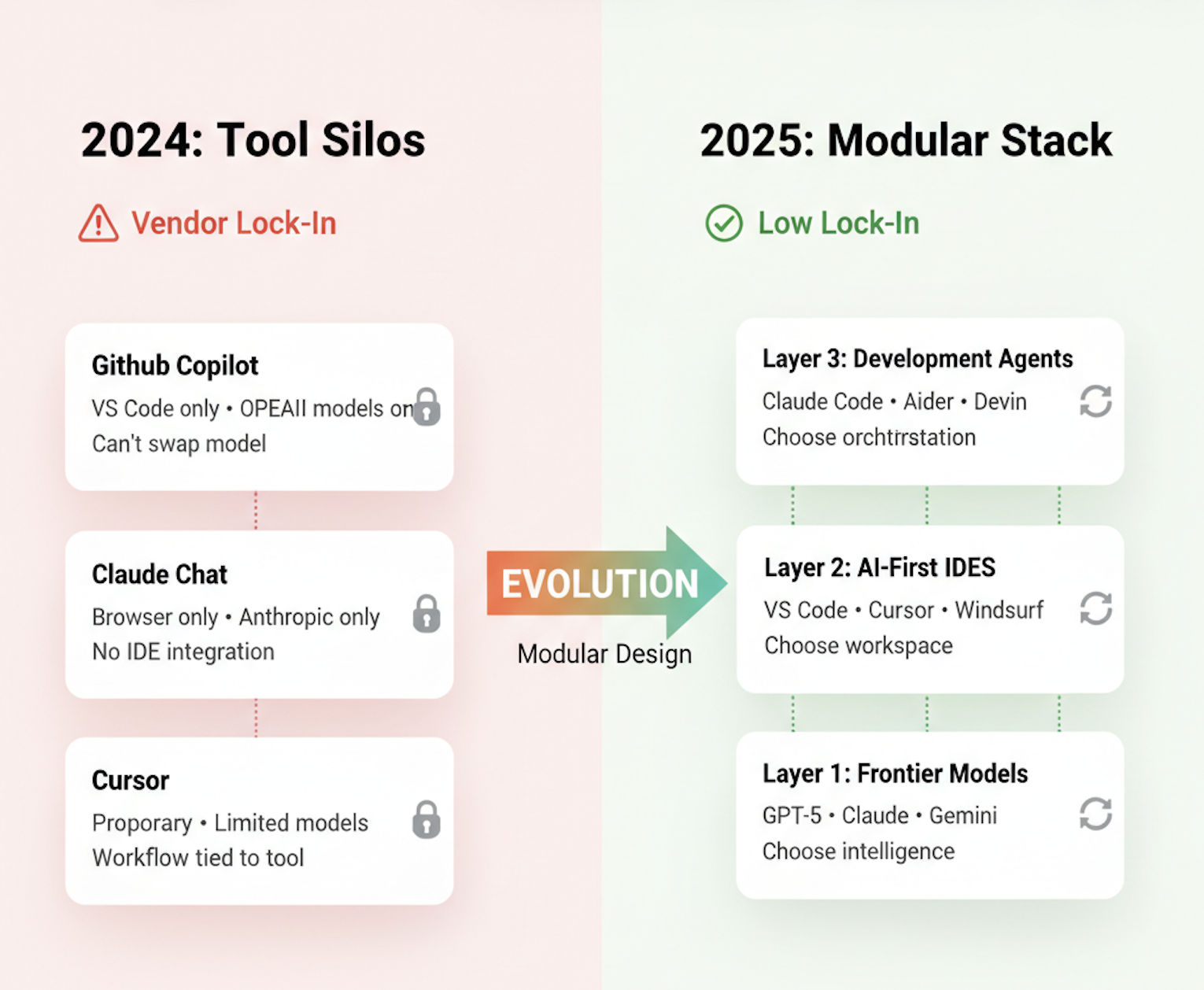
2024: Tool Silos
The Problem: Each tool was a monolith. GitHub Copilot only worked in VS Code and used OpenAI's models. Claude was a chat interface in a browser. If you wanted to use Claude's reasoning in VS Code, you couldn't. If Copilot raised its prices, you had no easy alternative.
The Result: Vendor lock-in. You picked a tool and hoped the vendor stayed competitive.
2025: Modular Stack
The Change: Three breakthroughs enabled the modular stack:
-
Model Context Protocol (MCP): A standardized way for AI tools to communicate with IDEs, databases, and other systems. Like USB for AI.
-
Frontier model APIs stabilized: Every major model (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Alibaba) now offers consistent APIs. You can swap models with minimal code changes.
-
AI-first IDEs matured: Editors like Cursor and Windsurf were built from the ground up for AI collaboration. They support multiple models and MCP natively.
The Result: Interoperability. You choose best-of-breed at each layer and compose them. Want Claude's reasoning in Cursor with Aider for autonomous execution? Done. Want to switch to Gemini 2.5 tomorrow? Change one configuration setting.
Comparison: 2024 vs 2025
| Dimension | 2024 | 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Monolithic tools (Copilot, Cursor) | Three-layer modular stack |
| Model Choice | Locked to vendor (Copilot = OpenAI only) | Swap models via API/MCP |
| IDE Flexibility | Tool dictates IDE (Copilot → VS Code) | Choose IDE, plug in any model |
| Vendor Lock-In | High (switching = relearning workflow) | Low (swap layers independently) |
| Autonomous Agents | Limited (early prototypes like Devin) | Production-ready (Claude Code, Aider) |
| Standardization | Proprietary protocols | MCP emerging as standard |
The Core Difference: In 2024, you chose a tool and adapted your workflow to it. In 2025, you choose layers and compose them to match your workflow.
🤝 Practice Exercise
Ask your AI: "I'm [beginner/intermediate], working on [type of projects], with [budget: free/paid]. Based on my context, help me choose: (1) Which frontier model should I start with? (2) Which AI-First IDE fits my situation? (3) Which development agent makes sense for my skill level? Explain the tradeoffs for each recommendation."
What you're practicing: Strategic tool selection—choosing the right stack layers based on YOUR specific context, not following generic "best tools" lists.
Model Context Protocol: Why It Matters
MCP is the glue that makes the three-layer stack possible. Here's why it's crucial:
The Problem Without MCP: Every AI tool needs to access your codebase, terminal, Git history, database, and external APIs. Without a standard, each tool builds custom integrations. Copilot has its own way of reading files. Cursor has another. Aider has a third. You can't mix and match.
The Solution With MCP: MCP defines a common language for AI tools to access resources. Your IDE supports MCP? Any MCP-compatible agent can read files, run commands, and access context—without custom integration.
Real-World Benefit: Say you start with Claude Code CLI (MCP-compatible) in VS Code. Six months later, a new agent (HypotheticalAI) launches with better performance. If it supports MCP, you switch with zero workflow changes. Your IDE, database, and Git integrations keep working.
The Analogy: MCP is like USB. Before USB, every device had a custom cable. After USB, you could plug any device into any port. MCP does the same for AI tools.
Current State (Late 2025): MCP is supported by Anthropic (Claude Code), some VS Code extensions, and Cursor. It's not universal yet, but adoption is growing. Expect most major tools to support it by 2026.
🎓 Expert Insight
The USB analogy for MCP is powerful, but here's the deeper lesson: Standards enable ecosystems, not monopolies. USB didn't make one device manufacturer win. It made all devices more useful. MCP does the same for AI tools. When you choose MCP-compatible tools, you're voting for an ecosystem where your choice matters more than vendor lock-in. This is why understanding architecture (three-layer stack) matters more than memorizing specific tools.
Choosing the Right Tools for Your Context
With the three-layer stack, you make three independent decisions:
Decision 1: Which Frontier Model? (Layer 1)
Factors to consider:
- Performance: GPT-5 and Claude Opus 4 lead in reasoning; Gemini 2.5 Pro has the largest context window.
- Cost: Gemini offers generous free tiers; Qwen Code is open-source and free to self-host.
- Privacy: Self-hosted models (Qwen) keep data on-premise; cloud models (GPT, Claude) require trust.
Quick Rule: Start with Claude Opus 4 (strong reasoning) or Gemini 2.5 Pro (free tier, massive context). Reassess every 6 months as new models launch.
Decision 2: Which AI-First IDE? (Layer 2)
Factors to consider:
- Existing skill: If you already use VS Code or JetBrains, stick with them and add AI extensions.
- AI-native experience: Cursor and Windsurf are built for AI-first workflows; they feel more integrated.
- Ecosystem: VS Code has the largest extension library; JetBrains excels for Java/Kotlin.
Quick Rule: If you're learning from scratch, try Cursor (AI-native, intuitive). If you have an existing IDE you love, add AI extensions to it.
Decision 3: Which Development Agent? (Layer 3)
Factors to consider:
- Autonomy level: Claude Code CLI and Devin handle complex multi-step tasks; Aider focuses on focused, supervised refactoring.
- Integration: Claude Code CLI integrates with MCP and Spec-Driven Development workflows (which this book teaches).
- Learning curve: Aider is lightweight and easy to start with; Claude Code CLI is more powerful but requires understanding subagents.
Quick Rule: Start with Claude Code CLI (this book's focus) or Aider (lightweight alternative). Graduate to more autonomous agents (Devin) as you gain experience.
The Question: "Every year there's a new 'revolutionary' tool or framework. JavaScript frameworks, no-code platforms, blockchain dev tools—they all promised to change everything. Isn't the three-layer AI stack just the latest fad? Why should I invest time learning this when it might be obsolete next year?"
The Reality: This skepticism is healthy. The tech industry has a history of overhyping new paradigms. But here's why the three-layer stack is different:
-
It's solving a real problem: Vendor lock-in and tool fragmentation are genuine pain points. Developers were already mixing ChatGPT, Copilot, and CLIs awkwardly. The stack formalizes what people were hacking together.
-
It's based on standards, not products: MCP is an open protocol, not a proprietary product. Standards (HTTP, USB, SQL) outlast products because they enable ecosystems, not lock-in.
-
The economics support it: Every major AI vendor (OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, Alibaba) benefits from interoperability—it expands the market rather than competing for lock-in. There's financial incentive to standardize.
-
It's already happening: As of late 2025, Claude Code, Cursor, VS Code, and Aider support MCP. This isn't vaporware; it's production-ready.
The Honest Risk: Yes, the specific tools will change. Claude Code might be replaced by something better in 2027. But the architecture is durable. The three-layer separation—models, interfaces, agents—reflects how AI-assisted development actually works. Even if the tools churn, the pattern remains.
What this means for you: Learn the three-layer concept, not just specific tools. Understand why separating models from IDEs from agents matters. That knowledge transfers even if Claude Code is replaced by HypotheticalAI in 2027.
Try With AI
Use your AI companion tool set up (e.g., ChatGPT web, Claude Code, Gemini CLI), you may use that instead—the prompts are the same.
Prompt 1: Discover Your AI Partnership Style
Let's explore how I naturally work with AI by reflecting on my experiences. Ask me: When have I used AI as an "advisor" (I ask questions, it suggests, I decide)? When have I used it as an "executor" (I describe what I want, it does the work)? Which felt more natural? Which produced better results? Help me discover MY partnership style—am I more comfortable with Layer 2 (collaborative suggestions) or Layer 3 (autonomous execution)? Don't prescribe—help me discover through reflection.
What you're learning: Self-awareness about your partnership preferences—understanding HOW you naturally collaborate with AI shapes which tools will work best for you.
Prompt 2: Explore AI's Three Roles In Your Work
AI can act as Teacher (suggests patterns you don't know), Student (learns from your feedback and preferences), and Co-Worker (collaborates with you). Let's explore which roles you experience most: Ask me questions about my AI interactions: "When has AI taught me something new? When has it adapted to MY style? When have we worked side-by-side collaboratively?" Help me discover which role I use LEAST and why. Then ask: "What's blocking you from leveraging that role more?"
What you're learning: Self-awareness about how you partner with AI—recognizing which interaction modes (teaching, learning, collaborating) you're underusing and why.
Prompt 3: Co-Design Your Stack Through Dialogue
I want to choose my AI development stack (frontier model + IDE + agent), but I don't want generic recommendations—I want choices that fit MY context. Share my situation with you: [experience level, project types, budget, learning goals]. Then ask me clarifying questions: "What matters most—cost, features, learning curve, or ecosystem?" "Do you have an IDE you already love?" "Are you building alone or with a team?" Based on my answers, co-create a stack recommendation. Let's iterate—you suggest, I ask "why?", you explain tradeoffs, we refine until I feel confident in the choices.
What you're learning: Strategic tool selection through bidirectional dialogue—not accepting recommendations passively, but co-creating decisions through exploration of tradeoffs.
Prompt 4: Future-Proof Your Learning Together
I'm worried about learning tools that become obsolete. Let's explore what's durable versus what's volatile. Ask me: "What am I trying to learn—specific tools or underlying concepts?" Then help me discover: What aspects of the three-layer stack are architectural patterns (durable) versus specific implementations (volatile)? Create a learning priority list WITH me: concepts to master (stay relevant), tools to experiment with (may change), patterns to recognize (transfer everywhere). Don't just tell me what to learn—help me discover the distinction through dialogue.
What you're learning: Distinguishing durable knowledge from volatile tools—your AI helps you identify what learning investments pay off long-term versus short-term.