Set Operations
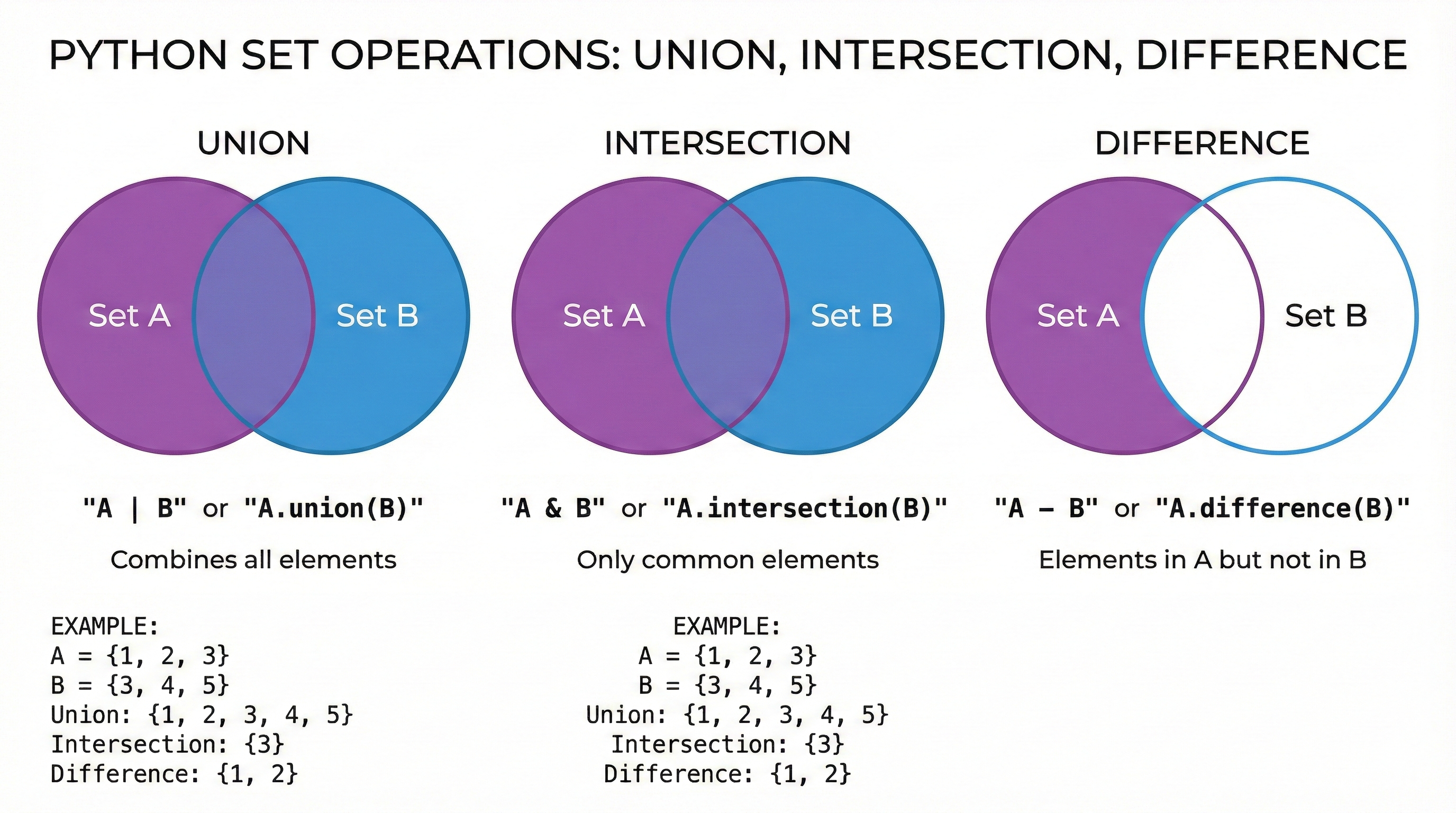
Now that you understand what sets are and how to create them, it's time to discover their real power. Sets aren't just useful for storing unique items—they're designed to perform mathematical operations on collections. In this lesson, you'll learn the four fundamental set operations that make sets essential for data comparison, filtering, and analysis.
When you need to find common interests between people, identify differences in datasets, or combine information without duplicates, set operations are your answer. And unlike many technical concepts, these operations have intuitive real-world meanings.
Set Operations: The Mathematical Foundations
Sets are based on mathematical set theory, which gives us four core operations. The beautiful part? Python makes these operations simple with elegant operator syntax.
Let's build our understanding progressively: start with the concepts, see them in code, then apply them to real problems.
Union: Combining Sets
Union combines elements from multiple sets into one set, keeping only unique items. It answers the question: "What items appear in any of these sets?"
Think of a music playlist: if you combine your favorite songs with your friend's favorite songs, union gives you all unique songs from both lists—no duplicates.
Code Example 1: Union Operations
Loading Python environment...
Key observation: Notice that "Alice" and "Bob" appear in both team_a and team_b, but in the result, they appear only once. That's the uniqueness property at work.
💬 AI Colearning Prompt
"In a real company with multiple departments, how would you use set union to find all employees across department A and department B? Could you have duplicates?"
Your AI can walk you through practical applications and help you see why union matters in business scenarios.
🎓 Expert Insight
In AI-native development, you don't memorize whether union is
|or.union()—both are correct. Your AI instantly reminds you. What matters is recognizing "I need to combine collections without duplicates" and choosing union.
Intersection: Finding Common Elements
Intersection finds elements that appear in all sets. It answers: "What items are in both sets?"
Imagine you're looking for bilingual developers. You have one set of Java developers and another set of Python developers. Intersection tells you who knows both languages.
Code Example 2: Intersection Operations
Loading Python environment...
Key observation: Intersection is commutative—A & B equals B & A. The order doesn't matter because we're finding what's in both.
🤝 Practice Exercise
Ask your AI: "I have two lists of customer IDs from two different marketing campaigns. I want to find which customers were in both campaigns. Use sets and intersection to solve this. Then explain why sets are better than lists for this task."
Expected Outcome: You'll see how intersection solves real business problems and understand why sets make this operation efficient.
Difference: Excluding Elements
Difference finds elements in the first set but not in the second. It answers: "What items are unique to the first set?"
Imagine a school where some students are graduating. Difference tells you which students are still enrolled (all students minus those who graduated).
Code Example 3: Difference Operations
Loading Python environment...
Key observation: Notice that A - B is different from B - A. The order matters because we're asking "what's in the first but not the second?"
Symmetric Difference: Elements in Either Set But Not Both
Symmetric Difference finds elements that appear in either set but not in both. It answers: "What items are unique to one set or the other?"
Think of two groups working different shifts. Symmetric difference tells you who never works with anyone from the other shift.
Code Example 4: Symmetric Difference
Loading Python environment...
Key observation: Symmetric difference is commutative—order doesn't matter. It's like XOR in logic: true if one or the other, but not both.
🎓 Expert Insight
Symmetric difference seems more complex than the others, but it answers a practical question: "What's different between these two datasets?" It's powerful for data reconciliation.
Set Comprehensions: Creating Filtered Sets
Just like list comprehensions, set comprehensions let you create new sets by filtering and transforming. They're a powerful pattern for creating derived sets.
Code Example 5: Set Comprehensions with Filtering
Loading Python environment...
Key advantage: Set comprehensions automatically eliminate duplicates. You get both filtering and deduplication in one expression.
Real-World Problem: Finding Common Interests
Let's combine everything we've learned to solve a realistic problem: matching users based on shared interests.
Code Example 6: Real-World Problem — Finding Common Interests
Loading Python environment...
This demonstrates: How set operations combine to solve real problems. Notice how we're chaining operations with | (union) and - (difference) to answer complex questions about relationships.
Practice: Master Set Operations
Try these exercises to build confidence with all four operations:
Exercise 1: Intersection Practice
You have two lists of students:
- Morning class:
["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "David"] - Afternoon class:
["Bob", "David", "Eve", "Frank"]
Convert to sets and find students in both classes using intersection.
Exercise 2: Union + Difference Chaining
You have inventory from three warehouses:
- Warehouse A:
{"Widget1", "Widget2", "Widget3"} - Warehouse B:
{"Widget2", "Widget4", "Widget5"} - Warehouse C:
{"Widget1", "Widget5", "Widget6"}
Find all unique widgets available across all warehouses (union), then find widgets that are in only one warehouse.
Exercise 3: Set Comprehension Challenge
Create a set of all odd numbers from 1 to 50 that are also greater than 20 using a set comprehension.
Exercise 4: Real-World Inventory Comparison
Two stores have product catalogs:
- Store A:
["Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Grape"] - Store B:
["Banana", "Orange", "Mango", "Pineapple"]
Find:
- Products both stores carry (intersection)
- All unique products across both stores (union)
- Products only Store A carries (difference)
Try With AI
Master set operations and comprehensions for data analysis.
🔍 Explore Set Operations:
"Show me Venn diagrams for union (|), intersection (&), difference (-), symmetric difference (^). For each operation, explain with overlapping circles, give real-world example (user permissions, course enrollment, inventory)."
🎯 Practice Operator vs Method:
"Help me compare operator vs method syntax: set_a | set_b vs set_a.union(set_b). Show both for union, intersection, difference. Explain when to use concise operators vs explicit methods."
🧪 Test Symmetric Difference:
"Debug symmetric difference: show A ^ B vs (A - B) | (B - A). Explain 'either but not both' concept with practical example. When is symmetric difference the clearest choice?"
🚀 Apply Set Comprehensions:
"Build set comprehension filtering strings > 4 chars and converting to uppercase. Explain syntax step-by-step. Compare to list comprehension version. Show how automatic deduplication differs."