Why Do Specs Matter NOW? The AI Moment
The Question
You've seen how vague code causes problems (Lesson 1). But specifications aren't new—they've existed since the 1970s.
So why is SDD only becoming standard practice NOW, in 2025?
If specs were so valuable, why didn't everyone use them 20 years ago?
What Changed: Three Convergent Forces
Three things happened simultaneously in 2025 that made specifications shift from "nice to have" to "essential":
1. AI Got Good Enough to Generate Production Code
Before 2025:
- AI-generated code was often broken, incomplete, or unreliable
- Developers spent more time fixing AI code than writing it themselves
- Result: Specs weren't worth the effort
2025+:
- LLMs can generate working, tested code from clear specifications
- Code quality jumped from "barely functional" to "production-ready"
- Result: Specs became the most efficient way to build software
2. Developers Discovered Specs Save Iteration Time
The Pattern Everyone Experienced:
-
Vague prompt: "Build a login system"
- Iteration 1: AI generates basic form (missing password reset)
- Iteration 2: Add password reset (missing rate limiting)
- Iteration 3: Add rate limiting (missing email verification)
- Iteration 4-10: Continue fixing missing requirements
- Total time: 10-12 hours
-
Clear spec: Explicit requirements document
- Iteration 1: AI generates complete system (all requirements specified)
- Iteration 2: Minor refinements
- Total time: 3-4 hours
Cost-Benefit Math:
Before: 2 hours vague prompt + 10 hours iteration = 12 hours
With SDD: 1 hour spec + 3 hours refinement = 4 hours
Savings: 8 hours (66% faster)
3. AI Agents Are Literal-Minded
Human developers can:
- Infer intent from context
- Ask clarifying questions during development
- Notice edge cases and flag them
- Work from sketches and vague requirements
AI agents can:
- Follow explicit instructions precisely
- CANNOT infer your unstated intent
- NEED unambiguous specifications
- Generate code exactly as described (no more, no less)
The Critical Insight:
With human colleagues, vague requirements were tolerated—they'd ask questions and fill gaps.
With AI agents, vague requirements produce incomplete code—they implement EXACTLY what you specified, missing everything you assumed.
Specifications became mandatory, not optional.
💬 AI Colearning Prompt
"Why do AI agents specifically need specs more than human developers do? What's different about how AI agents interpret requirements compared to human colleagues?"
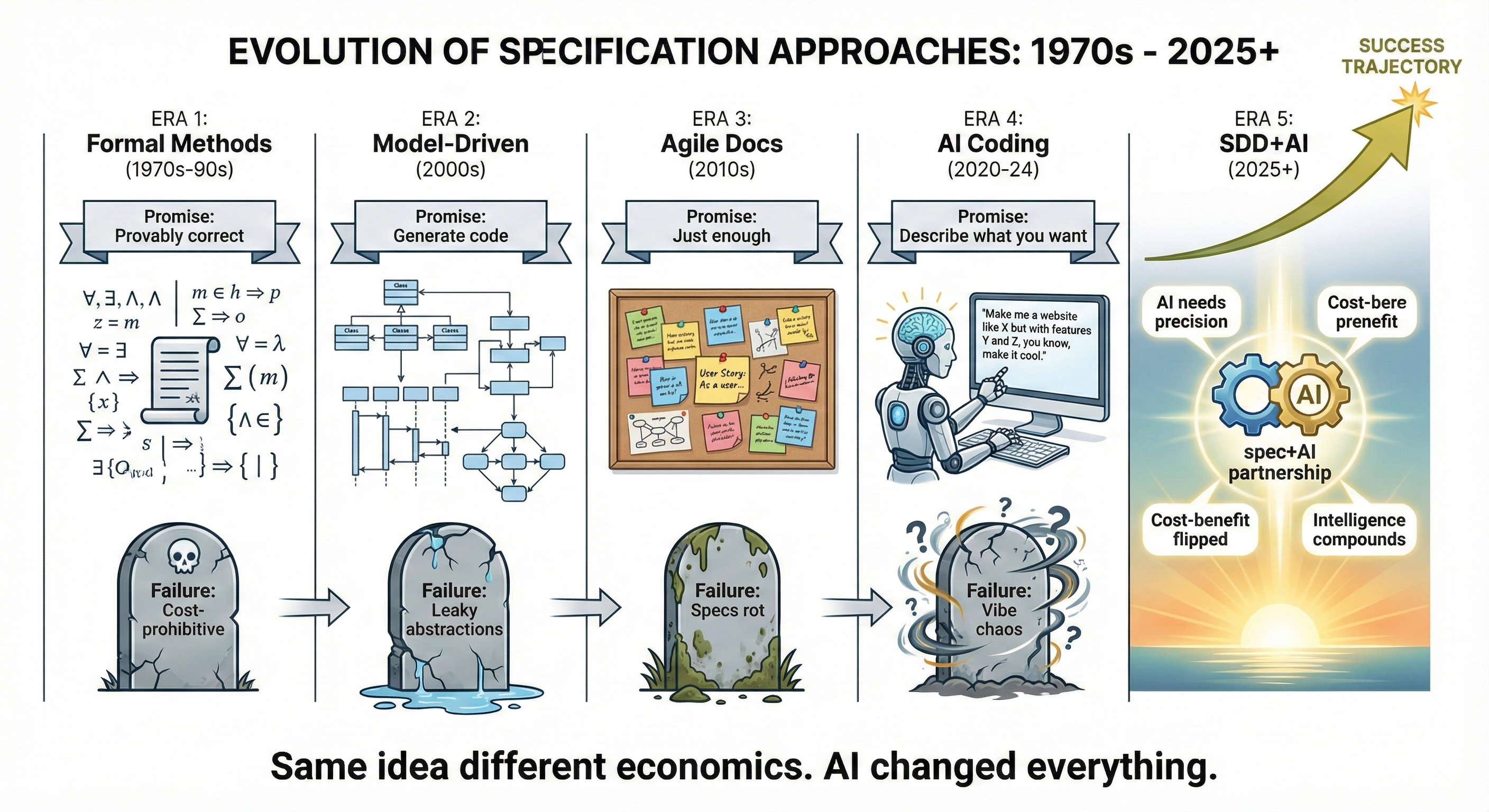
Historical Context: Why Specs Failed Before
Understanding why previous specification approaches failed helps us appreciate why SDD succeeds now.
1970s: Formal Methods
- Promised mathematically-proven correct code
- Failed because they required PhD-level math (impractical for most software)
- Lesson: Specs need to be accessible, not just rigorous
1980s: Design by Contract
- Promised specs embedded in code (pre/post conditions)
- Failed because it was language-specific (only Eiffel)
- Lesson: Specs need separation from implementation
2000s: Model-Driven Development (MDD)
- Promised specs (UML models) → automatic code generation
- Failed because tools created lock-in, models diverged from code, abstraction level was wrong
- Lesson: Natural language specs are more flexible than formal models
2010s: Agile Backlash
- Minimized specs to maximize iteration
- Failed because teams lost institutional knowledge, couldn't scale, documentation disappeared
- Lesson: No specs is also bad—balance is needed
2025+: SDD Emerges
What's different NOW?
- AI agents powerful enough to generate correct code from natural language specs
- AI agents literal-minded — NEED explicit specs (can't improvise like humans)
- Specs became the interface between humans and AI
- Cost-benefit finally works: Specs save measurable time with AI
The Specific Insight: AI Literal-Mindedness
Ask your companion:
Why do AI agents specifically benefit from specs? What's different about
how AI agents work compared to human colleagues?
Your companion will explain:
"Human colleagues can ask 'Did you want password reset?' when they notice it's missing.
AI agents implement EXACTLY what you specify. If you didn't mention password reset, the AI assumes you don't want it.
This isn't a limitation—it's how AI works. Specifications provide the explicit detail AI needs to generate complete systems."
The Key Shift:
- Before AI: Specs were nice but not essential (humans could improvise)
- With AI: Specs became essential (AI can't improvise)
This is why SDD emerged now. AI made specs mandatory.
🎓 Expert Insight
In AI-native development, specifications aren't overhead—they're the interface. Just as command-line expertise defined Unix mastery, specification-writing defines AI-native mastery. The developer who writes clearer specs gets better code, faster iteration, and fewer bugs. Spec quality IS code quality now.
Why SDD Succeeds Where MDD Failed
Model-Driven Development (MDD) promised automatic code generation in the 2000s. It mostly failed.
Why MDD Failed:
- Abstraction mismatch: Models sat at awkward level (too detailed for managers, too vague for developers)
- Tool lock-in: Custom code generators created dependency on specific vendors
- Incomplete models: Models didn't capture edge cases, developers hand-edited generated code
- Divergence: Code and models went out of sync (which is source of truth?)
Why SDD Succeeds:
- Natural language specs: More flexible than UML/DSL, accessible to all team members
- LLMs need no custom tools: Any LLM can generate code from natural language
- Less lock-in: Specs are markdown/prose, not proprietary format
- Faster feedback: Spec changes → regenerated code in minutes (not hours)
- Better models: 2024+ LLMs understand nuance and edge cases far better than 2004 code generators
Try With AI
Ready to understand why SDD emerged at this specific moment in history? Explore these prompts:
🔍 Explore Historical Context:
"Why did Model-Driven Development (MDD) fail in the 2000s, but Specification-Driven Development (SDD) succeeds now? What's different about LLMs vs. the code generators of 2005?"
🎯 Practice Cost-Benefit Analysis:
"Calculate the time savings for me: If I spend 1 hour writing a clear spec vs. 30 minutes on a vague prompt, how many iteration cycles do I need to break even? Show me the math."
🧪 Test Your Understanding:
"Compare three scenarios: (1) Human colleague gets vague requirements, (2) AI agent gets vague requirements, (3) AI agent gets clear spec. Predict what happens in each case and explain why AI needs specs more than humans do."
🚀 Apply to Your Experience:
"Think about my last 3 AI coding sessions. How many iterations did each take? If I had written a spec first, estimate how much time I would have saved. Be honest about the tradeoffs."