The Claude Code Origin Story and Paradigm Shift
You've probably heard this claim before: "AI makes coding faster."
Here's the uncomfortable truth: for most developers, AI coding tools actually slow them down.
Not because the AI is bad at writing code. Because the workflow creates friction. You're in your editor, you hit a problem, you switch to a browser, you describe your code to ChatGPT (without being able to show it), you get a response, you copy it, you paste it, you adapt it to your actual variable names, you test it, it fails, you go back to the browser, you describe the error (again, without showing your actual code)...
The AI never sees your project. Every conversation starts from zero. You become a human copy-paste bridge between two worlds that can't talk to each other.
What if there was a different approach? What if AI could simply see your code?
What Actually Happened at Anthropic
In September 2024, an engineer named Boris Cherny joined Anthropic and started an experiment. He gave Claude something it had never had before: direct access to the filesystem.
What happened next revealed something the team hadn't anticipated. When Claude could read files, it didn't just answer questions better—it explored. Given access to a codebase, Claude naturally started reading files, following imports, understanding project structure. The behavior emerged without explicit instruction.
Cherny had discovered what the team later called the "Product Overhang": the capability to be a genuine development partner already existed inside Claude. It was waiting. The model didn't need to become smarter. It needed a product that let it actually see what developers were working on.
This wasn't a feature request being fulfilled. This was a hidden capability being unlocked.
But would anyone else actually want to use it?
The Dogfooding Explosion
Many developers believe their peers resist new tools. Adoption is supposed to be slow. People stick with what they know.
In November 2024, Anthropic released the dogfooding version internally. Twenty percent of engineering adopted it on day one. By day five, that number hit fifty percent. By the time Claude Code launched publicly in May 2025, over eighty percent of Anthropic engineers were using it daily.
The productivity data was striking: engineers averaged five pull requests per day—compared to the typical one or two at most companies. The team size grew from two engineers to around ten, yet pull request throughput increased by sixty-seven percent, the opposite of what usually happens when teams scale.
As of mid-2025, Claude Code generates over $500 million in annual run-rate revenue. Not from marketing. From word-of-mouth and developers telling other developers.
Something about this tool spread faster than anyone predicted. The question is: what made the difference?
The Paradigm Shift: Agentic vs. Passive
The answer lies in a fundamental distinction most people miss when they first encounter AI coding tools.
Traditional AI assistants operate in a passive model. You describe your problem. AI generates a suggestion. You copy-paste. You adapt. You test. You repeat. The AI has no context about your actual code—it knows only what you tell it, which is never enough.
Claude Code operates in an agentic model. You describe your goal. Claude reads your actual files. It understands your project structure, your dependencies, your patterns. It proposes specific changes to specific files. With your approval, it executes those changes. It can run tests, see errors, and iterate.
Think of it this way: passive AI is a consultant giving advice over the phone. Agentic AI is a pair programmer sitting next to you, looking at your screen.
Understanding General Agents: The Trojan Horse
Here's a secret that changes how you think about Claude Code: calling it a "coding agent" is like calling a CEO an "email writer."
Yes, a CEO uses email. But email is just the interface. The real work is decision-making, strategy, and getting things done. Same with Claude Code. It uses code, but code is just how it exerts control over your computer.
Claude Code is a General Agent—an AI that can reason through problems, make plans, and take action across many domains. The terminal isn't a limitation. It's Claude Code's command center for controlling your entire digital world.
The Habitat Difference:
| Feature | Coding Assistant (Copilot) | General Agent (Claude Code) |
|---|---|---|
| Where it lives | Inside your text editor | In the terminal (your OS) |
| What it sees | Just the file you're editing | Your entire file system |
| What it does | Suggests text completions | Executes commands |
| Scope | "Complete this line" | "Solve this problem" |
A coding assistant lives in a text box. A General Agent has the keys to the machine.
How General Agents Think: The OODA Loop
Traditional AI assistants predict the next word. General Agents reason through problems.
When you ask ChatGPT a question, it predicts what text should come next based on your input. When you ask Claude Code to debug an error, it runs a reasoning loop:
- Observe: "I see an error in the logs. Let me read the error message."
- Orient: "This looks like a database connection issue. The config file might be wrong."
- Decide: "I'll check the database config file first."
- Act: reads config file, finds the problem
- Correct: "That wasn't it. Let me check environment variables instead."
This is called the OODA Loop (Observe, Orient, Decide, Act)—plus the critical addition of self-correction. Claude Code doesn't just respond once. It keeps going until the problem is solved.
Prediction vs Reasoning:
| Prediction (ChatGPT) | Reasoning (Claude Code) |
|---|---|
| "Based on your description, try X" | runs X, sees it fail, tries Y |
| Single response, then waits | Loops until goal is achieved |
| Can't verify its own suggestions | Tests its work, fixes mistakes |
| You adapt the output to your code | It adapts to your actual code |
This is why Claude Code feels different. It's not guessing what might help—it's working through the problem step by step, adjusting as it learns more.
General Agents vs Custom Agents: The Strategic Choice
In Part 6, you'll learn to build Custom Agents using SDKs like OpenAI Agents SDK and Google ADK. Here's how they differ:
| Aspect | General Agent (Claude Code) | Custom Agent (SDK-built) |
|---|---|---|
| Analogy | Senior consultant who figures things out | Factory machine for a specific task |
| Best for | Novel problems, debugging, exploration | Repetitive workflows, customer-facing |
| Flexibility | Handles anything you throw at it | Does one thing extremely well |
| Setup time | Instant (install and run) | Weeks (design and build) |
| Error tolerance | High (you review everything) | Low (must be reliable at scale) |
The powerful insight: You'll use Claude Code (a General Agent) to build Custom Agents. General Agents are the builders. Custom Agents are the products.
This is the Agent Factory model: your expertise + Claude Code + SDK = deployable product.
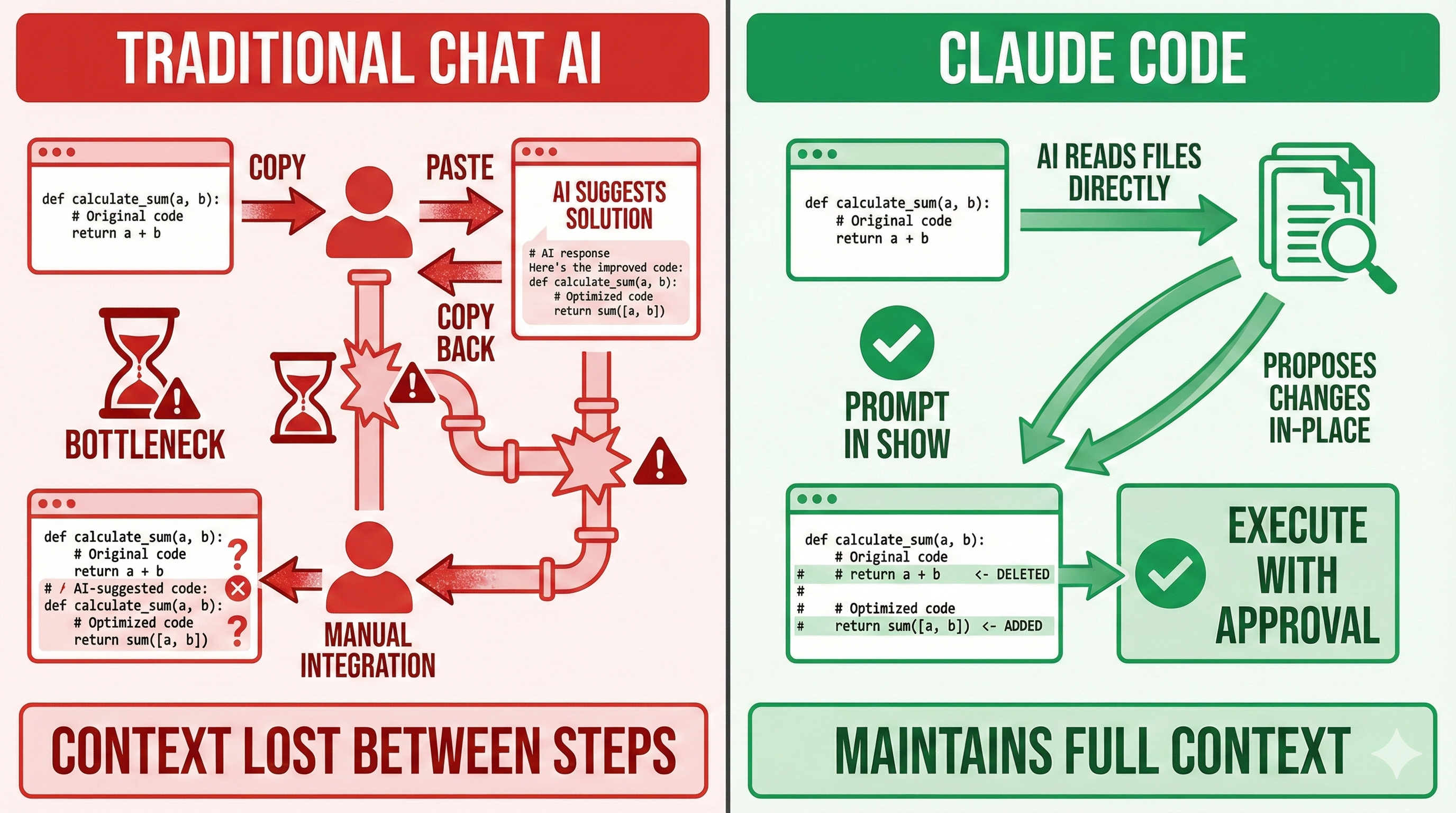
Comparison: Passive vs. Agentic AI Assistance
| Aspect | Passive AI (Chat-based) | Agentic AI (Claude Code) |
|---|---|---|
| Context Awareness | No access to your files; relies on your descriptions | Reads your actual codebase; understands project structure |
| Interaction Model | Q&A: You ask, AI answers | Collaborative: AI proposes, you approve, AI executes |
| Code Integration | Manual copy-paste and adaptation | Direct file modifications with version control |
| Error Handling | Generic troubleshooting advice | Specific debugging based on your actual code and logs |
| Workflow Interruption | Context-switch to browser; break flow | Stay in terminal; maintain development flow |
| Quality of Suggestions | Generic best practices | Project-specific solutions using your existing patterns |
| Learning Curve | Easy: just type questions | Moderate: requires terminal familiarity and trust |
But if agentic AI is so powerful, why does it need to live in the terminal?
Why Terminal Integration Matters
Some developers see "terminal-based AI" and think it's a niche preference—something for command-line enthusiasts. This misses the point entirely.
Terminal integration isn't a stylistic choice. It's what makes the agentic model possible.
Direct File System Access: The terminal is where your code lives. Claude Code can read your src/ folder, check your package.json, analyze your Git history—without you describing any of it.
Real-Time Execution: Claude Code can run your tests, execute scripts, see outputs, hit errors, and adjust. This feedback loop is impossible through a browser chat window.
Version Control Integration: Because Claude Code operates in the same environment as Git, changes are trackable and reversible. You see the exact diff before approving. Nothing happens without your explicit consent.
Workflow Alignment: Most development happens in terminals or terminal-integrated editors. Claude Code fits into your existing workflow instead of pulling you out of it.
Trust Through Transparency: Every command is visible. Every file change shows a diff. You're not trusting a black box—you're reviewing proposals and deciding what to accept.
The terminal isn't a limitation. It's the foundation that makes context-aware, action-capable AI possible.
Code Is the Universal Interface

Here's an insight that surprises many people: Claude Code isn't just for software development.
"Code" sounds like programming. But code is actually the universal interface to the digital world. We don't just write code to build software—we use code to interrogate reality.
Example: A Business Question
Your CEO asks: "Why did sales drop in Q3?"
A coding assistant would be useless here. But a General Agent?
- Writes SQL to fetch sales data from your database
- Writes Python to analyze trends and find patterns
- Creates a chart showing the drop happened in the Enterprise segment
- Reads customer churn data to correlate with the timing
- Reports: "Sales dropped because of 40% churn in Enterprise accounts, concentrated in August when we raised prices."
That's not "coding." That's using code as a tool to answer real questions.
Beyond Software: Any Domain
Through code, Claude can:
- Call APIs to pull data from any service
- Organize files in any format (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF)
- Analyze data with Python scripts
- Generate reports in any structure you need
- Automate workflows across any digital tool
Real examples:
| Domain | What Claude Code Can Do |
|---|---|
| Finance | Pull data from QuickBooks, reconcile accounts, generate audit reports |
| Legal | Extract clauses from contracts, compare document versions, find inconsistencies |
| Marketing | Analyze competitor websites, generate content calendars, track campaign metrics |
| HR | Process resumes, schedule interviews, generate offer letters |
| Education | Create quizzes from content, grade assignments, personalize learning paths |
The scaffolding is thin: Bash commands, file system access, and Python execution. That's all Claude Code needs to become useful for virtually any digital knowledge work.
Skills as Monetizable Assets
This is why the lessons ahead teach "skills" that work across domains—not just programming skills, but expertise in finance, marketing, legal, education, and more.
Claude Code is the platform. Your domain expertise is what makes it valuable.
When you create a Skill that automates financial audits, or legal contract review, or sales outreach—that's not just a productivity tool for yourself. That's intellectual property you can sell.
In Lesson 14 of this chapter, we'll show you exactly how Skills become revenue. For now, understand this: every Skill you create in this chapter is a potential product.
So what does this new paradigm actually produce?
The Self-Building Proof
There's a common belief that AI can assist with coding but can't build complex systems on its own.
Here's the fact that challenges that assumption: approximately ninety percent of Claude Code was written by Claude Code itself.
The team didn't just use Claude Code to help with development. They used it to build the product. Sixty to one hundred internal releases ship daily. One external npm release ships daily. The tool that developers use to build software was itself built by that same tool.
This isn't a marketing claim. It's the logical conclusion of the paradigm shift. When AI can see your code, understand your patterns, propose changes, run tests, and iterate on failures—when it operates as an agent rather than an oracle—it becomes capable of sustained, complex work.
The ninety percent statistic isn't about AI being smart enough. It's about AI finally having the access it needs to do what it was already capable of doing.
What does this mean for your future as a developer?
Try With AI
Test your understanding of the paradigm shift through active exploration.
🔍 Explore the Friction Problem:
"I currently use ChatGPT/Claude web for coding help. Walk me through ONE specific workflow where the copy-paste friction costs me time—maybe debugging an error, or integrating a new library. Then show me what that same workflow looks like with filesystem access. Be concrete: what do I type, what does the AI see, what's different?"
💡 Understand the Product Overhang:
"Boris Cherny discovered that Claude could already explore codebases—it just needed filesystem access. Help me understand this 'Product Overhang' concept. What other capabilities might be locked inside AI models right now, waiting for the right product to unlock them? Give me 2-3 examples of capabilities that exist but aren't accessible through current interfaces."
🎯 Challenge Your Assumptions:
"I'm skeptical that 90% of a complex tool could be built by AI. Push back on my skepticism: What specifically makes this possible? Is it because the AI is smarter than I think, or because the workflow enables something different? Help me understand what changed that made self-building realistic."
🚀 Apply to Your Context:
"I work on [describe: web apps / data pipelines / mobile development / etc.]. Based on the paradigm shift from passive to agentic AI, what specific parts of my workflow involve the most copy-paste friction? Where would filesystem access change things most dramatically?"
Note: When using AI tools that access your files, start with non-sensitive projects. Review proposed changes before accepting. The transparency of terminal-based tools makes this review straightforward—you see exactly what will change.